Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 8 is an important year in a student’s life and Maharashtra State Board Science is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 8 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete Maharashtra State Board Class 8 Science Book syllabus.

Q1. Complete the table
| Property of Metal | Use in everyday life |
| Ductility | Copper, Gold |
| Malleability | Lead, Copper |
| Conduction of heat | Silver |
| Conduction of electricity | Aluminum, Iron |
| Sonority | Silver, Iron |
Q2. Identify the odd term
a. Gold, silver, iron, diamond
b. Ductility, brittleness, sonority, malleability
c. Carbon, bromine, sulphur, phosphorus
d. Brass, bronze, iron, steel
Answer a: Diamond –It is a nonmetal, rest are metals.
Answer b: Brittleness –It is a property of non metals, the rest are properties of metals.
Answer c: Bromine –it is liquid, the rest are solids.
Answer d: Iron –Rest are mixtures
Q3. Write scientific reasons.
a. The stainless steel vessels in the kitchen have a copper coating on the bottom.
b. Copper and brass vessels are cleaned with lemon.
c. Sodium metal is kept in kerosene.
Answer a: The stainless steel vessels in the kitchen have a copper coating on the bottom because copper is a good conductor of heat.
Answer b : Copper and brass vessels are cleaned with lemon because lemon contains acid and copper and brass react with acid.
Answer c: Sodium metal is kept in kerosene because sodium reacts with air and it burns so to prevent reaction it is kept in kerosene.
Q4. Answer the following.
a. What is done to prevent corrosion of metals?
b. What are the metals that make the alloys, brass and bronze?
c. What are the adverse effects of corrosion?
d. What are the uses of Noble metals?
Answer a: To prevent corrosion of metals, layers of oil, grease, varnish and paint are applied on them. Also plating with another non corroding metal is done. Iron is arrested by zinc plating. Due to these processes, the contact of metal surfaces with air is lost and corrosion cannot occur as the chemical reaction cannot occur.
Answer b: A homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or a homogeneous mixture metal with nonmetals is called alloy. Alloys are made by mixing the constituent elements in, as per the requirement. For example, the stainless steel utensils used at home are made of an alloy of iron with carbon, chromium and nickel. The alloy bronze is formed from copper and tin.
Answer c: The uses of Noble metals are:
Q5. Three experiments to study the process of rusting are given below. Observe the three test tubes and answer the following questions.
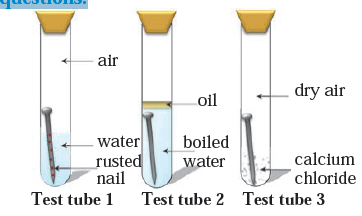
a. Why is the nail in the test tube 2 is not rusted?
b. Why is the nail in the test tube 1 rusted highly?
c. Would the nail in the test tube 3 get rusted?
Answer a: In the test tube 2 iron nail is not rusted due to cut off the supply of air by a layer of oil.
Answer b: The nail in the test tube 1 is rusted highly as it gets both air and moisture which is required for rusting.
Answer c: The iron nail in the test tube 3 is not rusted because of the calcium chloride which is moisture absorber. Hence, the nail would not get moisture for the rusting.
Q6. What are metals? Give examples .
Answer: Metals have a lustre and are hard. Wire or sheet can be made from metal. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. Metals lose their valence electrons to produce positively charged ions, that is, cations. Example: Gold, silver, iron, copper, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, sodium, platinum is a few metals.
Q7. What are nonmetals? Give examples.
Answer: Nonmetals are the elements which form negative ions by accepting or gaining electrons. Nonmetals usually have 4, 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their outermost shell. Example: Carbon, Sulphur, Phosphorus is a few nonmetals.
Q8. Write the physical properties of metals?
Answer: The physical properties of metals are:
Q9. Write chemical properties of metals?
Answer: The chemical properties of metals are:
Q10. Write the physical properties of nonmetals?
Answer: Some of the physical properties of non-metals are listed below.
Q11. Write chemical properties of nonmetals?
Answer: The chemical properties of nonmetals are:
Reaction with Water –Non-metal does not react with water but it is usually very reactive in air, which is why some of them are stored in water. For example, one of the highly reactive nonmetals is phosphorus and it catches fire when exposed to air. That is why it is stored in water to prevent its contact with atmospheric oxygen.
Reaction with Acids –None of the non-metals is known to react with acids.
Reaction with Bases –The reaction between non-metals and bases is a very complex one. The reaction of chlorine with bases like sodium hydroxide gives products like sodium hypochlorite, sodium chloride as well as water.
Reaction with Oxygen –Oxides of non-metals are formed when it reacts with oxygen. The oxides of non-metals are acidic or neutral in nature.
When sulphur reacts with oxygen, we get sulphur dioxide.
S + O2 → SO2
When sulphur dioxide reacts with water it forms sulphurous acid.
SO2 + H2 O → H2 SO3
Q12. Define noble metal.
Answer: Some metals like gold, silver, platinum, palladium and rhodium are noble metals. They occur in nature in the elemental state. Gold, which is100 percent pure is called 24 carat gold. Pure gold is soft. As a result, the ornaments made from pure gold bend or break due to pressure. Therefore, goldsmiths mix it with a certain proportion of copper or silver. Ornaments are made from 22 carat gold or gold with a still smaller carat value.
Q13. Define corrosion.
Answer: Gases in the air react with metals in the presence of moisture to form metal compounds. The metals get affected by this process and undergo what is called corrosion.
Q14. Explain uses of metals.
Answer: Metals are usually very strong, most durable and highly resistant to everyday wear and tear. As such, they have been used since ancient times for a lot of things. And even today with advances in technology and a lot of other things the uses of metals have broadened greatly. Metals even play a key role in the economy. Some of the important and popular metal uses are.
Q15. Explain uses of non-metals.
Answer: The uses of non-metals are:
Q16. Difference between metals and nonmetals.
Answer: The difference between metals and nonmetals are:
| Metals | Nonmetals |
| These are solids at room temperature except mercury | These exist in all three states |
| These are very hard except sodium | These are soft except diamond |
| These are malleable and ductile | These are brittle and can break down into pieces |
| These are shiny | These are non-lustrous except iodine |
| Electropositive in nature | Electronegative in nature |
| Have high densities | Have low densities |
Q17. How can we prevent corrosion?
Answer: We can prevent corrosion by the following ways:
Q18. What are the three types in which the elements are generally classified?
Answer: The three types in which the elements are generally classified are solids liquids gases
Q19. What are the metals and nonmetals that we use in everyday life?
Answer: Some non –metals and their uses are listed below-
Some metals and their uses are listed below:
Q20. What are non metal materials?
Answer: nonmetals are natural materials that do not produce heat or electricity and that are structurally brittle (can not be easily rolling, moulding, extruding or pressing). Chemically, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, arsenic, and selenium are the nonmetallic elements in the periodic table.